Diamond shape inheritance គឺជាការបន្តថ្នាក់ម៉្យាងដែលមានទំរង់ជាចតុកោណស្មើ ពោលគឺជាការបង្កើតថ្នាក់មួយបន្តភ្ជាប់ទៅនឹងថ្នាក់ពីរទៀត ដែលត្រូវបានតភ្ជាប់ទៅនឹងថ្នាក់តែមួយដូចគ្នា។ ពិនិត្យកម្មវិធីខាងក្រោមនេះ៖
class Geometry():
radian = 180
def display(self, info):
print(info)
class Surface(Geometry):
pi = 3.14
def __init__(self, *dimension):
self.dimension = dimension
def surface(self):
return self.dimension
class Volume(Geometry):
pi = 3.1415
def __init__(self, *dimension):
self.dimension = dimension
def volume(self):
return self.dimension
class Cube(Surface, Volume):
def __init__(self, width, height, depth):
Surface.__init__(self, width, height)
Volume.__init__(self, width, height, depth)
def surface(self):
dimension = Surface.surface(self)
s = dimension[0] * dimension[1] * 6
print("The cube's surface is", s)
def volume(self):
dimension = Volume.volume(self)
v = dimension[0] * dimension[1] * dimension[2]
print("The cube's volume is", v)
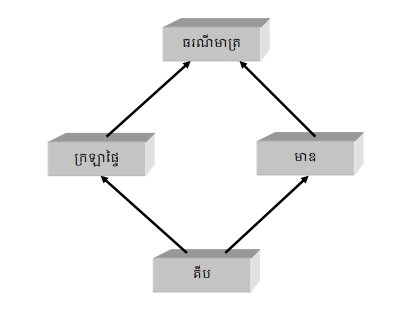
ការបន្តថ្នាក់តាមរបៀបដូចនៅក្នុងរូបខាងលើនេះ ត្រូវហៅថា diamond shape inheritance ពីព្រោះទំរង់របស់វាមានរាងជា diamond ឬចតុកោណស្មើ។
ក្នុងករណីមានការបន្តថ្នាក់មានរាងចតុកោណស្មើ នៅពេលដែល attribute ណាមួយត្រូវយកមកប្រើ ការស្វែងរក attribute នោះត្រូវធ្វើឡើងទៅតាមគំនូសបំព្រួញដូចខាងក្រោមនេះ៖
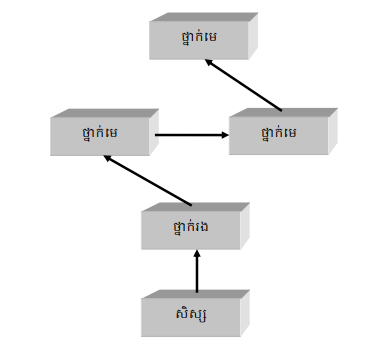
មានន័យថា នៅពេលដែល attribute ណាមួយត្រូវយកមកប្រើតាមរយៈ instance ឬថ្នាក់ណាមួយ ការស្វែងរកវត្ថុនោះ ត្រូវធ្វើឡើងនៅក្នុង instance នោះមុន រួចបានឡើងទៅថ្នាក់ផ្សេងៗទៀត តាមសញ្ញាព្រួញរហូតដល់ attribute នោះត្រូវរកឃើញ។ ពិនិត្យកម្មវិធីខាងក្រោមនេះ៖
class Geometry():
radian = 180
def display(self, info):
print(info)
class Surface(Geometry):
pi = 3.14
def __init__(self, *dimension):
self.dimension = dimension
def surface(self):
return self.dimension
class Volume(Geometry):
pi = 3.1415
def __init__(self, *dimension):
self.dimension = dimension
def volume(self):
return self.dimension
class Cube(Surface, Volume):
def __init__(self, width, height, depth):
Surface.__init__(self, width, height)
Volume.__init__(self, width, height, depth)
def surface(self):
dimension = Surface.surface(self)
s = dimension[0] * dimension[1] * 6
print("The cube's surface is", s)
def volume(self):
dimension = Volume.volume(self)
v = dimension[0] * dimension[1] * dimension[2]
print("The cube's volume is", v)
cube = Cube(25, 5, 10)
cube.surface()
cube.volume()
print('The value of pi is', cube.pi)


